Introduction:
In the ever-expanding landscape of technology, few concepts have captured the collective imagination as profoundly as the metaverse. This sprawling digital universe, where individuals can interact, create, and explore in entirely virtual realms, has undergone a remarkable evolution from the realm of science fiction to tangible virtual environments. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll trace the origins, pivotal moments, and future implications of the metaverse, drawing from both historical milestones and contemporary developments.
Origins in Science Fiction:
The seeds of the metaverse were sown in the fertile imaginations of science fiction visionaries. Neal Stephenson’s groundbreaking novel “Snow Crash,” published in 1992, is often cited as a seminal work that popularized the term and introduced the concept of a vast, interconnected virtual world where users could engage in myriad activities. Stephenson’s depiction of the Metaverse, a virtual reality-based successor to the internet, laid the conceptual groundwork for envisioning a future where digital spaces transcend the limitations of physical reality.
Early Virtual Worlds:
The advent of the internet facilitated the development of early virtual worlds that laid the foundation for the metaverse. Platforms like Second Life, launched in 2003, and Active Worlds, which debuted in 1995, provided users with rudimentary yet groundbreaking experiences in creating avatars, interacting with others, and building virtual environments. These pioneering platforms demonstrated the potential of virtual spaces to serve as social hubs and avenues for creative expression, albeit within the constraints of early technology.
Growth of Massively Multiplayer Online Games (MMOs):
The proliferation of massively multiplayer online games (MMOs) played a pivotal role in advancing the evolution of the metaverse. Games such as World of Warcraft, launched in 2004, EverQuest (1999), and RuneScape (2001) introduced millions of players to immersive virtual worlds teeming with vast landscapes, quests, and vibrant communities. These virtual environments served as precursors to the interconnected, persistent universes envisioned in the concept of the metaverse, offering glimpses of the social and interactive potential of digital spaces.
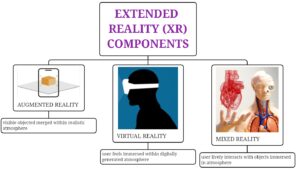
Virtual Reality Renaissance:
The resurgence of virtual reality (VR) technology in the early 21st century marked a significant milestone in the evolution of the metaverse. With the advent of affordable VR headsets such as the Oculus Rift (2016), HTC Vive (2016), and PlayStation VR (2016), users gained unprecedented access to immersive digital experiences that blurred the boundaries between physical and virtual reality. This technological leap brought the metaverse closer to realization by enabling more immersive, interactive, and sensory-rich environments, accelerating the convergence of virtual and physical worlds.
Blockchain and Decentralized Virtual Worlds:
The integration of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of decentralized virtual worlds, further propelling the evolution of the metaverse. Projects like Decentraland, launched in 2017, and Cryptovoxels leverage blockchain to create digital landscapes where users have ownership rights over virtual land and assets. By leveraging blockchain’s transparency, security, and decentralization, these platforms empower users to participate in user-driven economies, engage in creative expression, and forge novel forms of social interaction within the metaverse.
Future Implications and Challenges:
As the metaverse continues to evolve, it presents a myriad of opportunities and challenges for society at large. On one hand, it offers unprecedented avenues for creativity, collaboration, and entertainment, revolutionizing industries ranging from gaming and entertainment to education and commerce. The metaverse holds the potential to reshape the way we live, work, and play, offering immersive experiences that transcend geographical boundaries and physical limitations.

Let’s delve into the history of the metaverse, exploring its evolution through significant milestones year by year:
1. **1992: “Snow Crash” Introduces the Metaverse**: Neal Stephenson’s novel “Snow Crash” popularizes the term “metaverse” and introduces the concept of a vast, interconnected virtual reality where users can interact and engage in various activities.
2. **1995: Launch of Active Worlds**: Active Worlds, one of the earliest virtual worlds, is launched, allowing users to create avatars and build virtual environments. It becomes a precursor to more sophisticated virtual platforms.
3. **2003: Second Life Launches**: Linden Lab launches Second Life, a massively multiplayer online world where users can create, buy, and sell virtual property, socialize, and engage in various activities. It becomes one of the most popular virtual worlds of its time.
4. **2004: World of Warcraft**: Blizzard Entertainment releases World of Warcraft, a massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) that becomes immensely popular and introduces millions of players to immersive virtual worlds.
5. **2010: Emergence of Oculus Rift**: Palmer Luckey unveils the Oculus Rift, a groundbreaking virtual reality headset that ignites renewed interest in VR technology and lays the foundation for future advancements in immersive experiences.
6. **2014: Facebook Acquires Oculus VR**: Facebook acquires Oculus VR, signaling the tech giant’s investment in virtual reality and its potential applications beyond gaming.
7. **2017: Launch of Decentraland and Cryptovoxels**: Decentraland and Cryptovoxels are launched, leveraging blockchain technology to create decentralized virtual worlds where users have ownership rights over virtual land and assets.
8. **2019: VRChat and Rec Room Gain Popularity**: VRChat and Rec Room, social VR platforms that enable users to interact and create content in virtual environments, gain widespread popularity, showcasing the growing interest in social virtual experiences.
9. **2020: COVID-19 Pandemic Accelerates Virtual Engagement**: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates the adoption of virtual engagement platforms as people seek alternative ways to socialize, work, and attend events remotely.
10. **2021: Epic Games Announces Metaverse Ambitions**: Epic Games, the developer of Fortnite, announces its ambitions to build a metaverse, signaling mainstream recognition of the concept and its potential beyond gaming.
11. **2022: Microsoft’s Acquisition of Activision Blizzard**: Microsoft’s acquisition of Activision Blizzard, a major player in the gaming industry, including the popular virtual world platform World of Warcraft, underscores the growing importance of virtual experiences and the metaverse in the tech industry.
12. **2023: Meta Platforms Rebrands Facebook to Meta**: Meta Platforms, formerly known as Facebook, rebrands itself to Meta, signaling its commitment to building the metaverse and expanding its focus beyond social media.
These milestones reflect the gradual evolution of the metaverse from its conceptual origins in science fiction to tangible virtual environments that are increasingly integrated into our daily lives. As technology continues to advance and societal attitudes towards virtual experiences evolve, the metaverse is poised to become an integral part of how we interact, create, and explore in the digital age.
The metaverse encompasses a vast and interconnected network of virtual spaces, each comprising different domains and layers that interact to create a seamless digital environment. Understanding the relationship between these domains and layers is crucial for comprehending the complexity and depth of the metaverse. Here’s a breakdown of the relationship between various domains and layers within the metaverse:
1. **Domains**:
Domains in the metaverse represent distinct virtual spaces or environments, each with its own unique characteristics, purposes, and rules. These domains can range from social hubs and gaming worlds to educational platforms and virtual marketplaces. Examples of domains include virtual reality games like Fortnite, social platforms like Decentraland, and collaborative workspaces like Spatial.
2. **Layers**:
Within each domain of the metaverse, there are multiple layers that define different aspects of the virtual experience. These layers interact with each other to create immersive and interactive environments for users. The following are common layers found within the metaverse:
– **Spatial Layer**: The spatial layer defines the three-dimensional layout and structure of the virtual environment. It encompasses elements such as landscapes, buildings, objects, and avatars, allowing users to navigate and interact with the virtual space.
– **Social Layer**: The social layer facilitates communication, collaboration, and interaction among users within the virtual environment. It includes features such as chat systems, voice communication, friend lists, and social gestures, enabling users to engage with each other in real-time.
– **Economic Layer**: The economic layer governs the virtual economy within the metaverse, encompassing activities such as buying, selling, trading, and earning virtual assets and currencies. It includes features such as virtual marketplaces, digital currencies, and mechanisms for asset ownership and exchange.
– **Content Layer**: The content layer encompasses user-generated and curated content within the virtual environment, including games, experiences, artworks, and multimedia. It provides users with a diverse range of entertainment, educational, and creative opportunities, fostering engagement and exploration.
– **Identity Layer**: The identity layer defines how users are represented and identified within the virtual environment. It includes features such as user profiles, avatars, customization options, and authentication mechanisms, allowing users to express themselves and maintain their digital identity.
– **Technological Layer**: The technological layer comprises the underlying infrastructure, software, and hardware that power the metaverse. It includes technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), blockchain, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI), enabling the creation and operation of immersive virtual experiences.
3. **Interactions**:
The domains and layers of the metaverse are interconnected and interact with each other to create a cohesive and dynamic virtual ecosystem. Users navigate between different domains, interacting with various layers to engage in activities, socialize with others, create content, and participate in the virtual economy. For example, users may explore a virtual world (spatial layer), communicate with friends (social layer), purchase virtual goods (economic layer), create and share content (content layer), customize their avatar (identity layer), and leverage immersive technologies (technological layer) all within a single domain of the metaverse.
In summary, the relationship between domains and layers within the metaverse is symbiotic, with each contributing to the overall richness and complexity of the virtual experience. By understanding and harnessing these relationships, developers, creators, and users can unlock the full potential of the metaverse as a transformative platform for interaction, collaboration, and creativity.
Conclusion:
The evolution of the metaverse represents a remarkable journey from the realms of science fiction to the forefront of technological innovation. What was once a distant dream articulated by visionary authors has now become an increasingly tangible reality, thanks to advancements in virtual reality, blockchain technology, and online connectivity. As we navigate this brave new world of digital immersion, it is imperative to remain mindful of the opportunities, challenges, and ethical considerations that accompany it. By embracing the potential of the metaverse while addressing its associated complexities, we can harness its transformative power to chart new frontiers in the boundless realm of virtual reality.

